 Read article: Wobbling pulsar discovered
Read article: Wobbling pulsar discovered
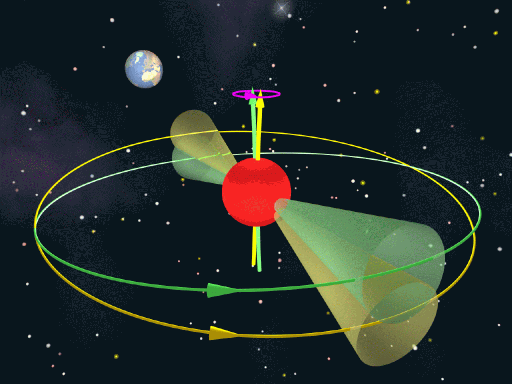
Wobbling pulsar discovered
Pulsars are rotating neutron stars, and are the collapsed cores of supergiant stars that have exploded as supernovae. They are extremely dense, typically 20 km across but with masses a million times g...

